南湖新闻网讯(通讯员 王文韬)近日,湖北洪山实验室、作物遗传改良国家重点实验室周道绣教授课题组在The Plant Cell 杂志在线发表题为“SnRK1 stimulates the histone H3K27me3 demethylase JMJ705 to regulate a transcriptional switch to control energy homeostasis”的研究论文,揭示了组蛋白去甲基化酶JMJ705参与水稻能量稳态调节的相关表观遗传学机制。
能量稳态对于所有生命都至关重要。与动物相比,植物需要更为复杂的适应机制以应对不断变化的环境,而能量稳态调节作为环境适应最为重要的一环,涉及到非常复杂的调控通路。真核生物含有一类在进化上极其保守的激酶复合体SNF1,其在能量稳态的调节中扮演着核心调控因子的角色,这类激酶在植物中被称之为SnRK1。SnRK1一般通过对其他蛋白进行磷酸化修饰来进行能量相关信号的传导与调控。当能量供应不足时,SnRK1可以调节相关基因的转录来促进植物能量生成,降低能量消耗以维持能量供需平衡。早期研究发现SnRK1可以直接结合染色质,然而SnRK1如何作用于染色质,进而参与基因表达的调控机制仍不清楚。
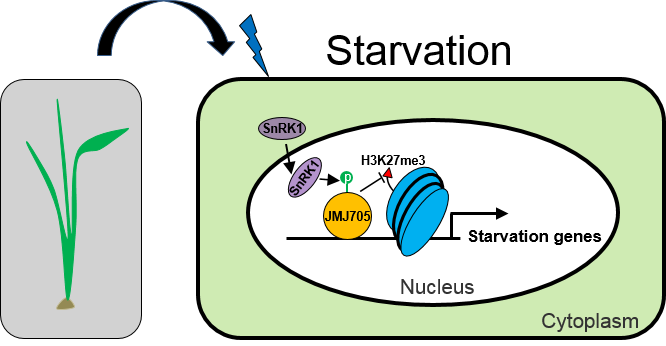
本研究发现,当水稻处于饥饿状态时,饥饿信号促使SnRK1在细胞核中富集,与组蛋白H3K27me3去甲基化酶JMJ705发生相互作用,并对JMJ705进行磷酸化修饰,提高其去除H3K27me3修饰的能力,降低饥饿应答基因座位上的H3K27me3修饰水平,从而促进这些基因的表达,维持细胞中足够的能量供应;在能量充足的情况下,SnRK1与JMJ705协同抑制饥饿诱导基因的表达,减少植物对能量的消耗以保证正常生长发育。本研究鉴定的SnRK1-JMJ705通路在植物细胞能量调节、染色质修饰以及基因表达调控之间建立起了直接的联系,加深了人们对作物生长发育与逆境应答之间平衡关系的认识,对于提高作物产量与环境适应性研究有重要的启发意义。
华中农业大学生命科学技术学院、作物遗传改良国家重点实验室和湖北洪山实验室周道绣教授课题组博士生王文韬作为该文第一作者,周道绣教授为文章通讯作者,赵毓教授也参与了本研究。本研究得到国家自然科学基金重点项目“水稻能量稳态调控相关的表观遗传调控机制研究”的支持, 是该项目框架下的第4篇研究论文,其它三篇分别是Zhang et al., (2017) Nuclear Acids Research; Lu et al., (2018) Genome Biology; Xu et al., (2021) Nuclear Acid Research。
【英文摘要】
Plant SNF1-Related Kinase1 (SnRK1) is an evolutionarily conserved energy sensing protein kinase that orchestrates transcriptional networks to maintain cellular energy homeostasis when energy supplies become limited. However, the mechanism by which SnRK1 regulates this gene expression switch to gauge cellular energy status remains largely unclear. In this work, we show that the rice histone H3K27me3 demethylase JMJ705 is required for low energy stress tolerance in rice plants. The genetic inactivation of JMJ705 resulted in similar effects as those of the rice snrk1 mutant on the transcriptome, which impair not only the promotion of the low energy stress-triggered transcriptional program but also the repression of the program under an energy-sufficient state. We show that the α−subunit of OsSnRK1 interacts with and phosphorylates JMJ705 to stimulate its H3K27me3 demethylase activity. Further analysis revealed that JMJ705 directly targets a set of low energy stress-responsive transcription factor genes. These results uncover the chromatin mechanism of SnRK1-regulated gene expression in both energy-sufficient and -limited states in plants and suggest that JMJ705 functions as an upstream regulator of the SnRK1α-controlled transcriptional network.
原文链接:
https://academic.oup.com/plcell/advance-article/doi/10.1093/plcell/koab224/6366557
相关文章链接:
https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/45/21/12241/4157412
https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13059-018-1533-y
https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/49/8/4613/6219121#234917398
审核人:赵毓
