南湖新闻网讯(通讯员 谢静)近日,我校工学院光机电共性技术与装备团队在南瓜幼苗耐盐等级评估研究中取得进展,相关研究成果以“Salt stress estimation in pumpkin germplasm based on maximum likelihood statistical modeling of the leaf color space distribution”为题在Computers and Electronics in Agriculture期刊上在线发表。
土壤盐渍化问题严重影响了作物的产量及品质,选育出抗盐南瓜品种作为砧木进行嫁接成为提高瓜类作物抗盐性的有效方法。目前,判断南瓜幼苗盐胁迫程度的方法主要为人工评级以及实验室理化分析,然而这些方法人力成本高,时效性差且结果易受主观判断的影响,精确度较低,结果重复性差。因此迫切需要一种更加科学便捷的检测方法进行南瓜幼苗盐胁迫程度检测,方便研究人员更好地进行选种育种。
针对上述问题,本研究通过统计分析南瓜幼苗真叶图像的各色彩通道反射强度的归一化最大似然值,设计了盐胁迫状态指数(β)来量化表征盐胁迫水平。基于β因子与盐害指数SI之间的非线性关系构建了南瓜幼苗耐盐等级评估模型,同时引入了叶片纹理因子(α)来区分叶片结构特征信息。研究发现,β值能够有效地反映叶片中的叶绿素相对含量变化,进而揭示盐胁迫对叶片生理状态的影响,α因子在聚类分析中发挥了重要作用,能够有效区分不同的簇,显著提高了模型的精度。该理论模型的数学结构仅需数据能覆盖全部特征,对样本总体量要求不高,可合理控制实验成本。同时,该理论模型可以精细解析南瓜幼苗在不同盐害程度下的RGB色彩空间的统计规律及真叶表面纹理特征,为进一步通过基因分析手段探讨纹理改变或叶绿素合成等相对基因调控网络对盐胁迫的响应方式提供思路,具有很好的应用前景。相较于传统的盐害评估方法,本研究提出的方法具有显著优势,其效率更高且更为客观,能够快速、精准地识别南瓜幼苗所遭受的盐胁迫水平。
华中农业大学工学院光电信息科学与工程专业21级本科生张欣焱和刘泉副教授为论文共同第一作者,华中农业大学工学院谢静副教授和园艺园林学院别之龙教授为论文共同通讯作者。华中农业大学园林学院硕士研究生李帅、工学院硕士研究生冯桦熊,工学院谭佐军教授、罗亮副教授、沈环副教授等参与了本项研究。该研究得到了国家自然科学基金和园艺作物种质创新与利用全国重点实验室项目的支持。
基于上述进展,谢静副教授和刘泉副教授指导工学院光电信息科学与工程专业22级本科生刘卓然开发了一款南瓜种质耐盐性智能巡检仪,以解决目前耐盐检测中存在的“检不快”和“评不准”的问题,实现了对于南瓜幼苗“巡—停—识—拍—传—评—巡”采集自动一体化流程,该设备获得2025年第十届国际大学生智能农业装备创新大赛一等奖,相关软件申请了软件著作权。
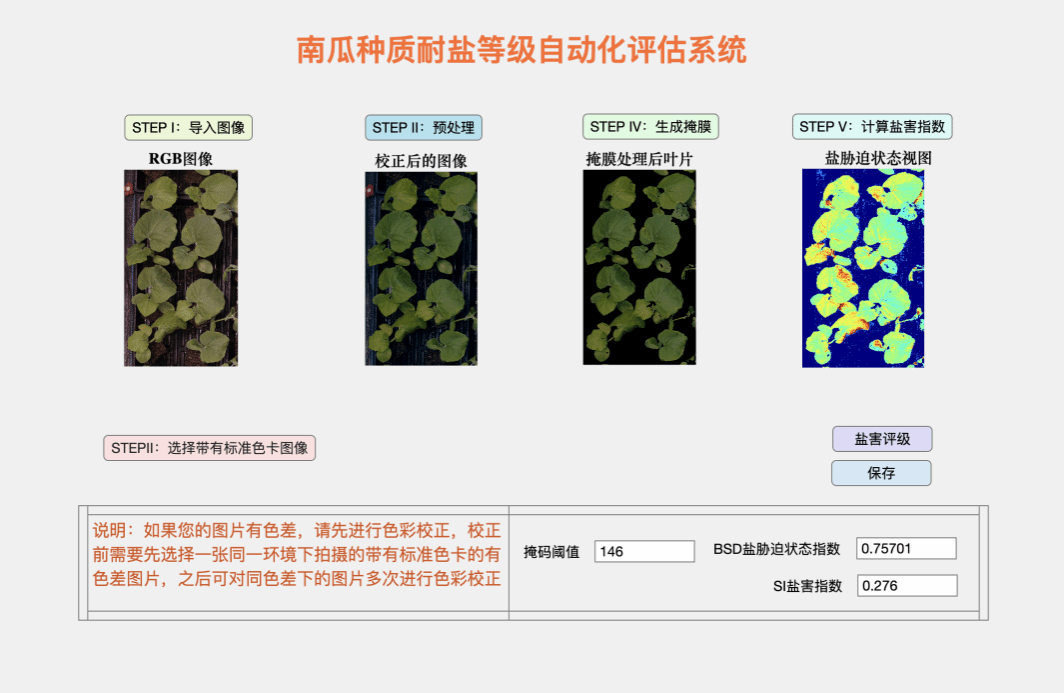
南瓜种质耐盐等级自动化评估软件
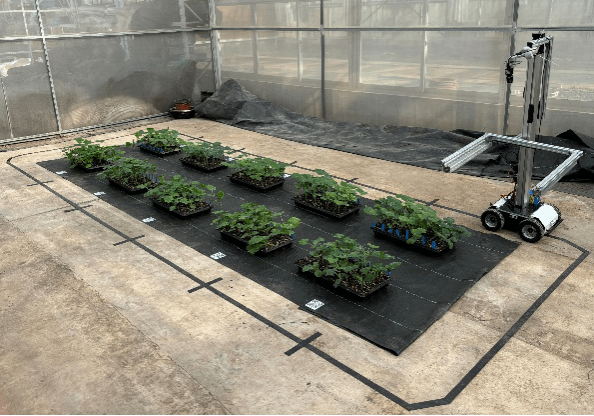

南瓜种质耐盐性智能巡检仪
论文链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2025.110982
英文摘要:Breeding salt-tolerant pumpkin cultivars is crucial for improving crop quality and yield. In this study, a high-resolution imaging-based phenotyping platform was developed to capture true leaf images of pumpkin seedlings subjected to salt stress, and plant experts conducted field assessments to determine the severity of salt damage. After image preprocessing, binary mask images were generated, and the maximum likelihood values of normalized intensity were extracted in the red, green, and blue channels to establish a salt stress status index (β) for characterizing stress levels. The β value shows a strong correlation with SPAD value, which indicates that it can effectively reflect the chlorophyll content in leaves, thereby reflecting the physiological changes in leaves affected by salt stress. A leaf texture factor (α) was employed to investigate the directional characteristics of the leaf texture, it can facilitate the effective differentiation of the clusters identified in the clustering analysis and enhance model precision by incorporating detailed leaf structural features. The performance of machine learning, deep learning, and statistical modeling approaches was compared. Statistical model integrating β and α exhibited superior predictive accuracy, with a coefficient of determination, root mean square error, and mean absolute error of 0.901, 0.057, and 0.046, respectively, in the validation dataset. Accuracy assessment among 49 germplasm accessions achieved 95.65 %, demonstrating the model’s reliability. Compared to conventional salt injury assessment, this approach offers higher efficiency and greater objectivity, enabling rapid and accurate identification of salt stress levels in pumpkin seedlings. This study provides a rapid and efficient method for assessing salt stress in pumpkin seedlings, contributing to a deeper understanding of stress response mechanisms and facilitating the selection of salt-tolerant cultivars. Moreover, these findings offer a valuable reference for salt stress identification in other plant species.
审核:谭佐军