南湖新闻网讯(通讯员 樊懿楷)近日,我校动物科学技术学院、动物医学院农业动物遗传育种与繁殖教育部重点实验室、农业农村部畜禽智慧养殖技术重点实验室张淑君教授团队在多种品牌傅立叶变换中红外光谱(Fourier Transform Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy, FT-MIRS)测定仪器间的校准转移方法及应用策略研究中取得进展。相关成果以 “Innovative calibration transfer methods and comprehensive application strategies for multi-brand FT-MIRS instruments in milk component analysis” 为题,发表于农业工程领域国际期刊Computers and Electronics in Agriculture。
傅立叶变换中红外光谱技术是一种通过识别有机物分子中化学键的振动特征来实现成分定量与定性的分析方法。凭借检测批量、高效、准确、低耗、绿色、无创和可同时测定多种指标等优势,FT-MIRS 在牛奶成分分析、食品质量控制、环境监测、工业生产以及智慧农业等领域被广泛应用。特别是在奶业领域,该技术已成为牛奶生产性能测定(DHI)的重要检测手段,为奶牛的遗传评估、群体改良和精准饲养提供了关键支撑。
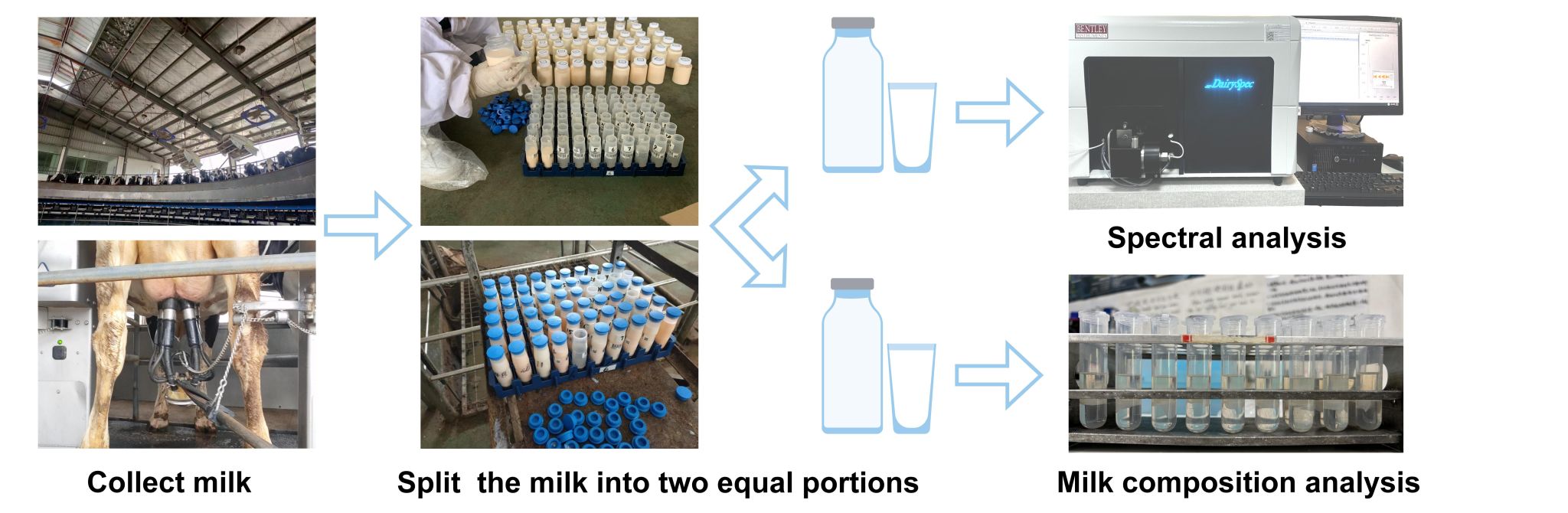

牛奶数据集收集和分析流程
然而,在实际应用中,由于不同品牌和型号的FT-MIRS仪器在光学部件、光谱分辨率、波段范围、数据采集方式等方面存在差异,直接导致同一检测对象在不同仪器上的光谱曲线不完全一致。这种差异会使得基于某一台仪器建立的预测模型无法直接迁移到另一台仪器上使用,影响了数据的整合和模型的共享。如何在多品牌仪器之间实现稳定、准确的模型校准与转移,成为国际上亟需解决的技术难题。
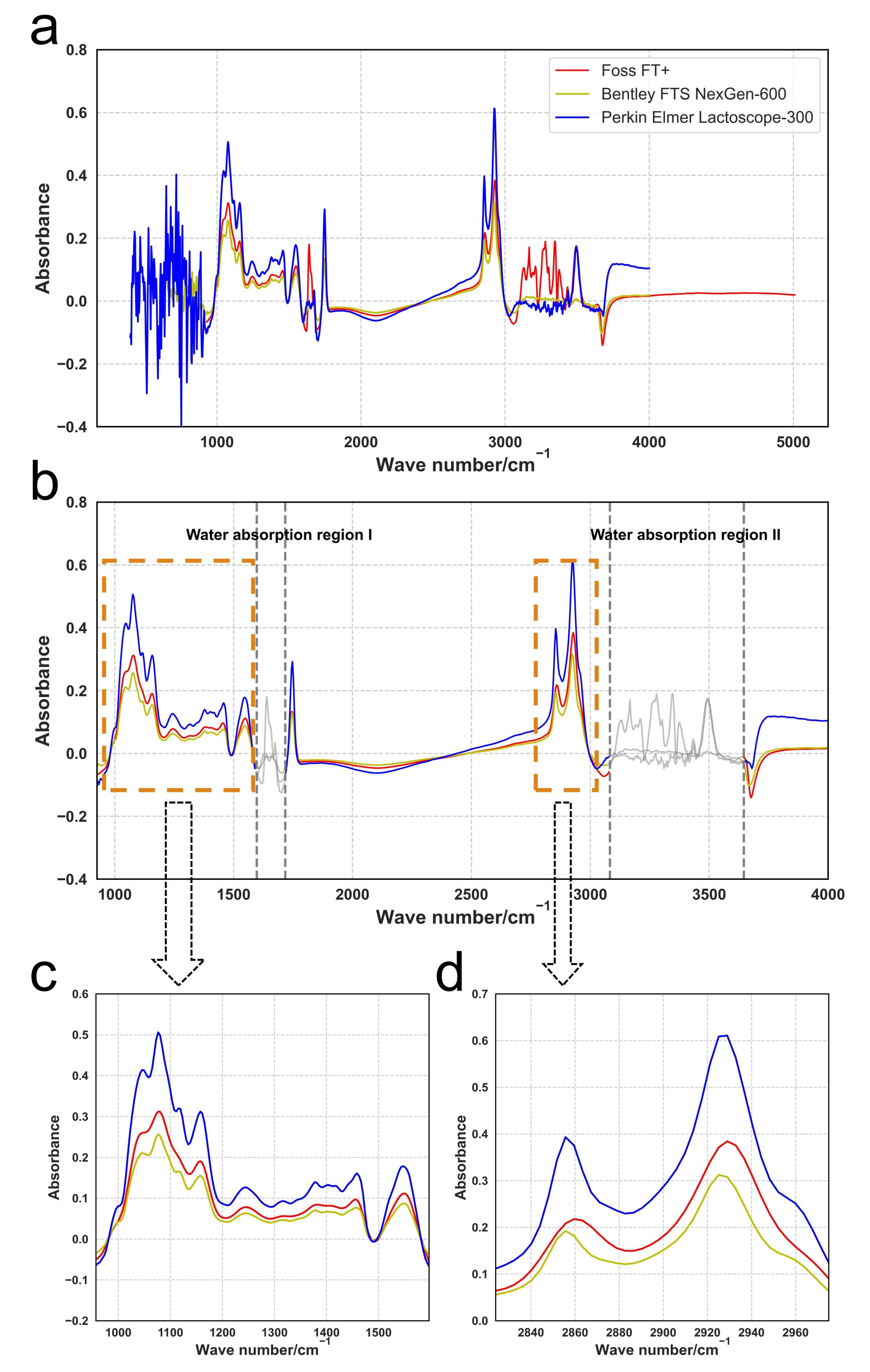
不同品牌仪器光谱差异
针对这一瓶颈问题,张淑君教授团队以Foss、Bentley和Perkin Elmer三种国际常用FT-MIRS仪器采集的乳成分数据为研究对象,综合考虑了光谱差异、算法特性与实际应用需求,系统评估了六种主流及改进型的校准转移方法,包括分段直接标准化(PDS)、单波数标准化(SWS)、凝聚聚类后分段直接标准化(ACPDS)、典型相关分析(CCA)、斜率与偏差校正(SBC)以及基于深度学习的光谱迁移方法(DTS)。在建模算法方面,团队采用了偏最小二乘回归(PLSR)、加权集成(Weighted Ensemble)和卷积神经网络(CNN)三种代表性方法,并构建了多种组合方案进行对比分析。
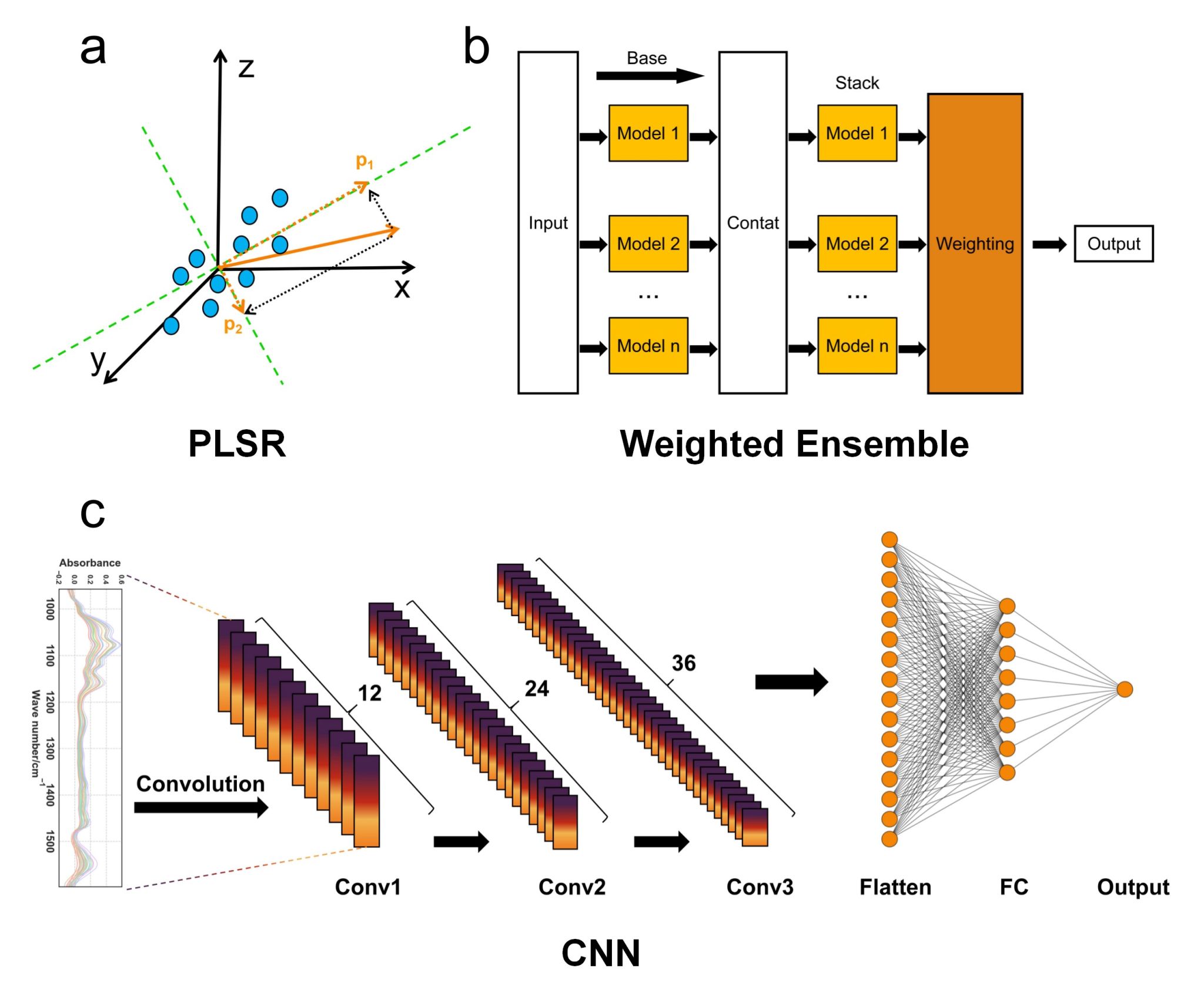
三种建模算法
研究结果表明,不同算法与校准转移方法的组合在跨仪器迁移性能上存在显著差异。其中,CNN结合PDS的组合在多种乳成分数据集和不同仪器间均表现出稳定且优异的性能,能够有效减少因仪器差异带来的预测精度下降。同时,团队首次验证了基于DTS的光谱模型迁移方法在FT-MIRS领域的可行性,该方法在缺乏标准样本的条件下依然表现出较好的适应性,尤其适用于设备条件受限或无法同步测定标准样本的场景。通过大规模的随机抽样测试,团队还验证了不同方法在不同仪器类型上的稳定性和适配性,并据此提出了针对不同品牌、不同数据集类型的FT-MIRS仪器间校准转移应用策略。
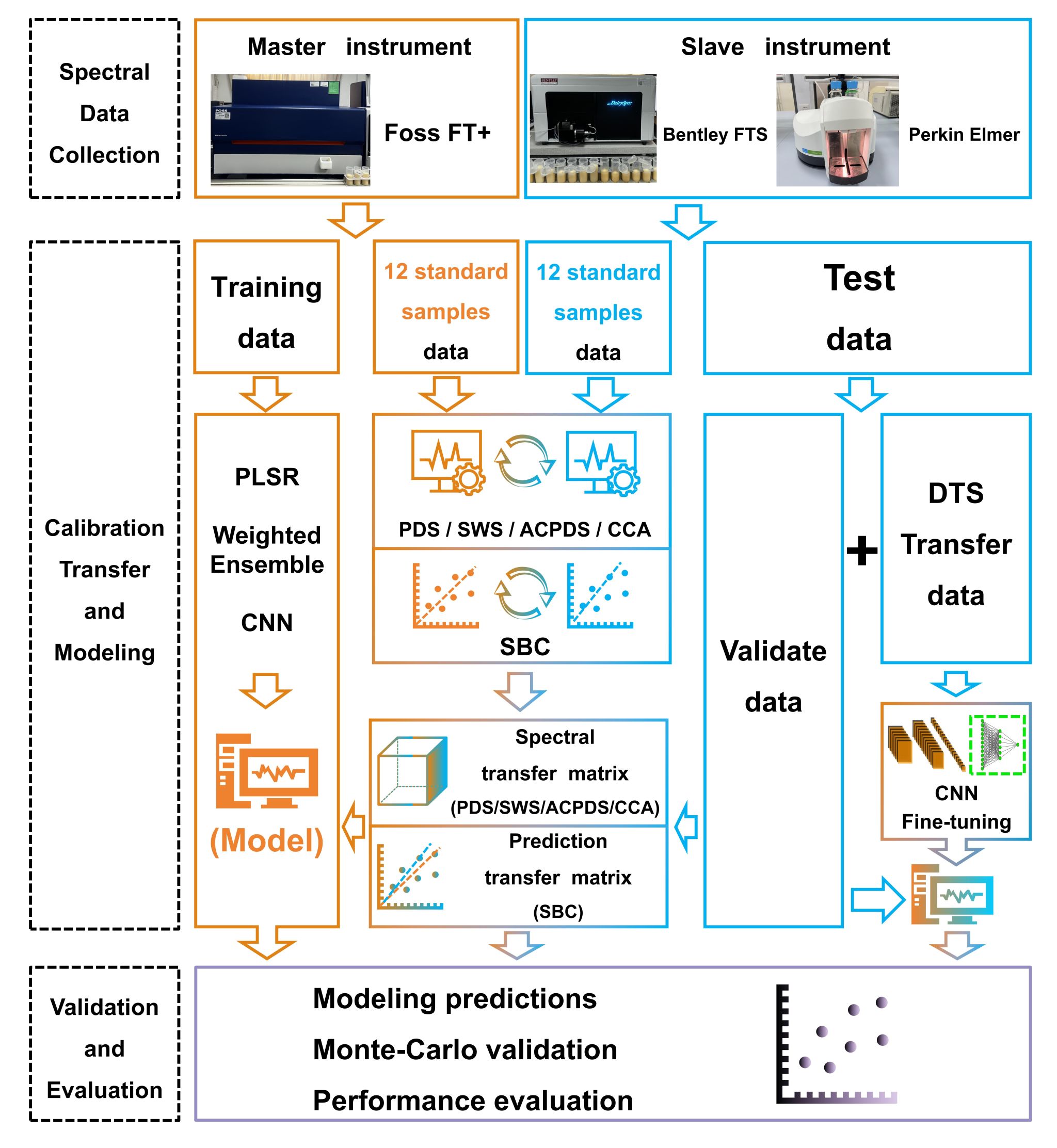
实验设计与分析流程
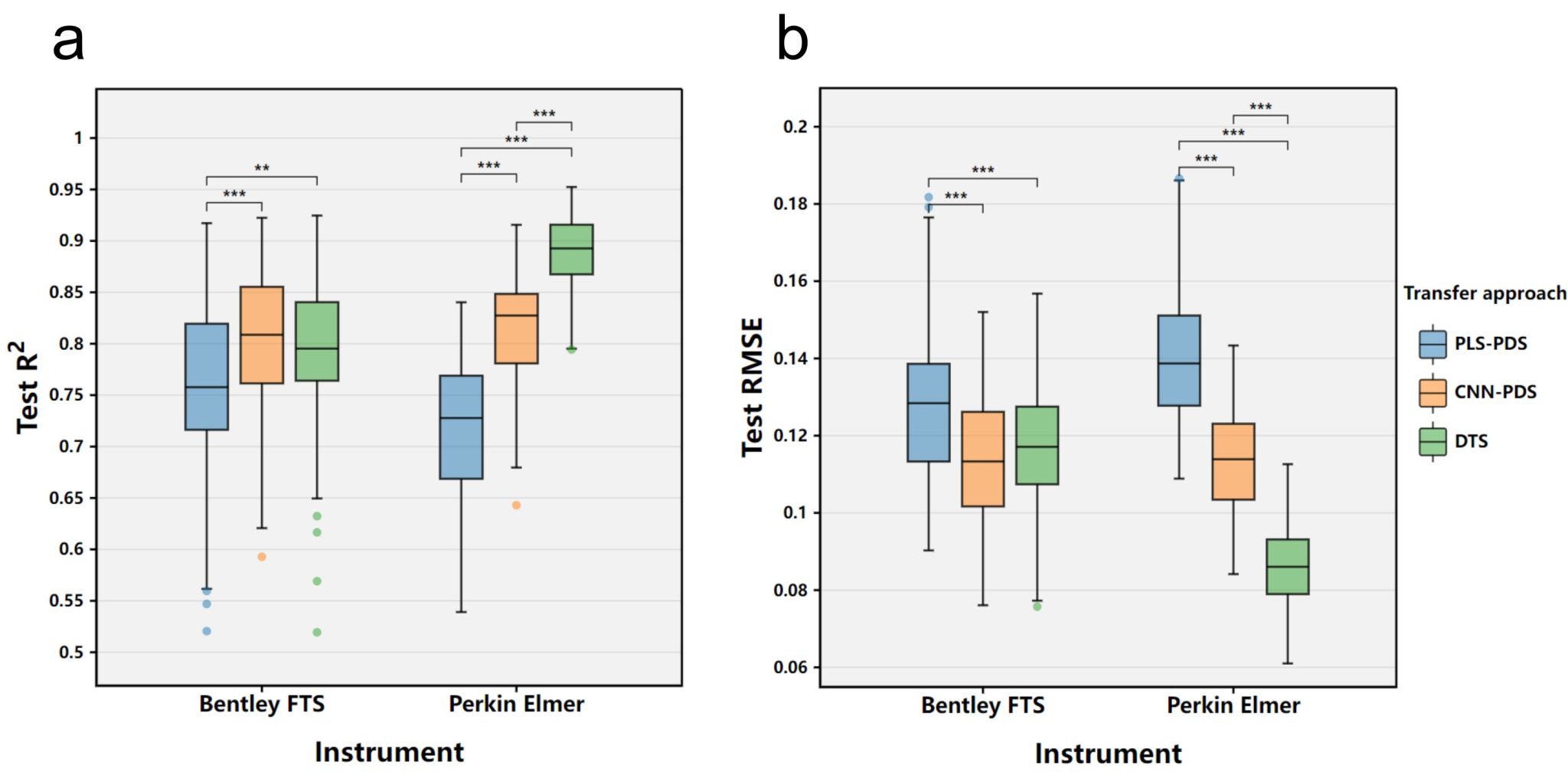
不同校准转移组合方法在不同品牌仪器上的稳定性和适配性
该成果不仅为FT-MIRS预测模型在多品牌仪器间的推广应用提供了高效可行的技术路径,也为建立跨仪器、跨地区、跨时间的大规模乳业数据平台奠定了重要基础。未来,这一方法体系有望推广至其他液态有机物检测及相关农业生产领域,进一步提升数据共享和模型复用的效率,对推动我国乃至全球的奶牛育种改良、乳品质量检测和智慧农业发展具有重要意义。
我校动科动医学院已毕业博士樊懿楷为论文第一作者,信息学院李嘉位老师与动科动医学院张淑君教授为共同通讯作者,全国畜牧总站刘刚、刘婷婷、白文娟和刘瑶等为共同作者。该研究得到了国家重点研发计划项目(2023YFE1300400)、国家乳业创新中心项目(2022-KYGG-3)和国家自然科学基金青年基金(32402825)等资助。
论文链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2025.110889
英文摘要:
Fourier Transform Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-MIRS) is highly effective in identifying functional groups or chemical bonds in organic compounds. It is widely utilized in analytical chemistry, industrial production, and smart agriculture. While calibration transfer methods have demonstrated their efficacy in decreasing spectral variations between instruments, the diversity in configurations remains a significant hurdle for data fusion analysis. Therefore, this study focuses on three milk component datasets(total protein, total fat and total solids) and combines three modeling algorithms (Partial Least Squares Regression (PLSR), Weighted Ensemble, and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)) for the research and testing of six calibration transfer methods (Piecewise Direct Standardization (PDS), Single wave number Standardization (SWS), Agglomerative Clustering Piecewise Direct Standardization (ACPDS), Canonical Correlation Analysis (CCA), Slope and Bias Correction (SBC), and Deep Transfer Spectra (DTS)) among three instrument brands (Foss, Bentley, and Perkin Elmer).
The results indicate that employing the CNN algorithm to develop prediction models on the master instrument (Foss) yields optimal performance when coupled with the PDS calibration transfer method across the three milk component datasets (referred to as the CNN-PDS combination). The R2 values range from 0.599 to 0.859, with an average of 0.769 for test data after calibration transfer. Additionally, it is validated that the DTS method, which is independent of standard sample dependence, is still applicable and shows significant improvement potential among FT-MIRS instruments. Particularly noteworthy is its highest performance, with an R2 of 0.894 on the protein dataset of the Perkin Elmer instrument. Furthermore, Monte Carlo random testing further verifies the adaptability and stability of CNN-PDS and DTS to Bentley and Perkin Elmer, respectively. Finally, the research findings lead to the proposal of application strategies for calibration transfer methods among different brands of FT-MIRS instruments, marking the first such recommendations. These strategies advocate for the judicious selection of the optimal transfer scheme for modeling algorithms (PLSR or CNN) and calibration transfer methods (PDS, ACPDS, or DTS) based on considerations such as dataset characteristics, experimental conditions, and instrument brand type. This study develops and summarizes effective FT-MIRS calibration transfer schemes and usage strategies. It provides technical and theoretical foundations for the utilization of predictive models across multiple brands of FT-MIRS instruments, as well as for FT-MIRS calibration transfer and its application in diverse fields.
审核人:张淑君