南湖新闻网讯(通讯员 涂特)近日,我校工学院晏水平教授团队在国际期刊Applied Energy上发表题为“CO2 regeneration energy requirement of carbon capture process with an enhanced waste heat recovery from stripped gas by advanced transport membrane condenser”的研究成果。研究创新性地提出了融合先进跨膜冷凝器的改进型富液再生技术,并构建了真实二氧化碳再生试验系统,实现了二氧化碳再生能耗的大幅下降,为烟气、沼气等气体的碳捕集过程的节能降耗提供了重要参考。
碳捕集、利用和储存(CCUS)技术是实现碳中和目标的支撑技术之一,其关键之一在于低成本CO2捕集。CO2化学吸收技术作为一种现阶段可大规模商业化运行的技术,存在富CO2吸收剂溶液(简称富液)再生能耗高等关键瓶颈问题亟待解决。在富液的热再生阶段,从再生塔顶排出的再生气由水蒸气和CO2组成,含有大量的潜热。如能高效回收此部分余热,将有助于降低再生能耗。经典的富液分流技术主要通过分流的冷富液与再生气的直接接触来回收再生气中的余热,余热回收性能较差,节能降耗效果不明显。
本研究创制了先进的跨膜冷凝器,其由具有纳米级膜孔的亲水陶瓷膜与不锈钢壳体组合而成。同时,构建了融合跨膜冷凝器的改进型富液分流热再生试验系统(图1)。在该系统中,分流富液与热再生气在跨膜冷凝器的陶瓷膜两侧逆向运行,并通过热再生气中的水热耦合传递,实现再生气余热回收性能强化。研究中,对比了传统CO2再生、经典富液分流再生及融合跨膜冷凝器的改进型富液分流再生等三种技术的CO2再生能耗。与传统CO2再生相比,在乙醇胺吸收剂体系中采用经典富液分流再生技术时,CO2再生能耗仅降低约4.8%,而采用本研究提出的融合跨膜冷凝器的改进型富液分流再生技术时,CO2再生能耗降幅可大幅提升至21.7%(图2)。同时,融合跨膜冷凝器的改进型富液分流再生技术还能降低CO2捕集系统的总冷却水耗量,具有节水潜力。
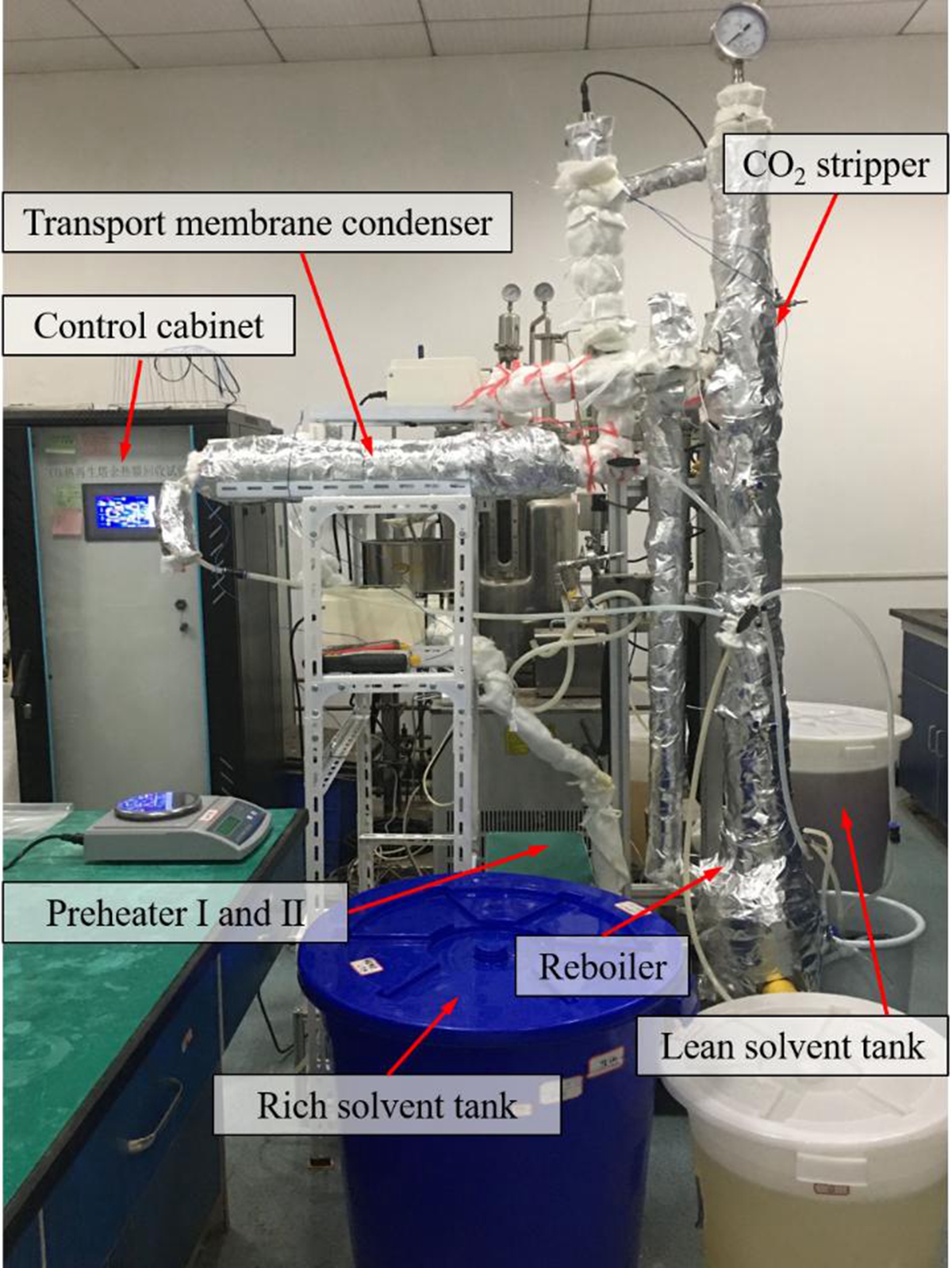
图1 融合跨膜冷凝器的改进型富液分流再生试验系统
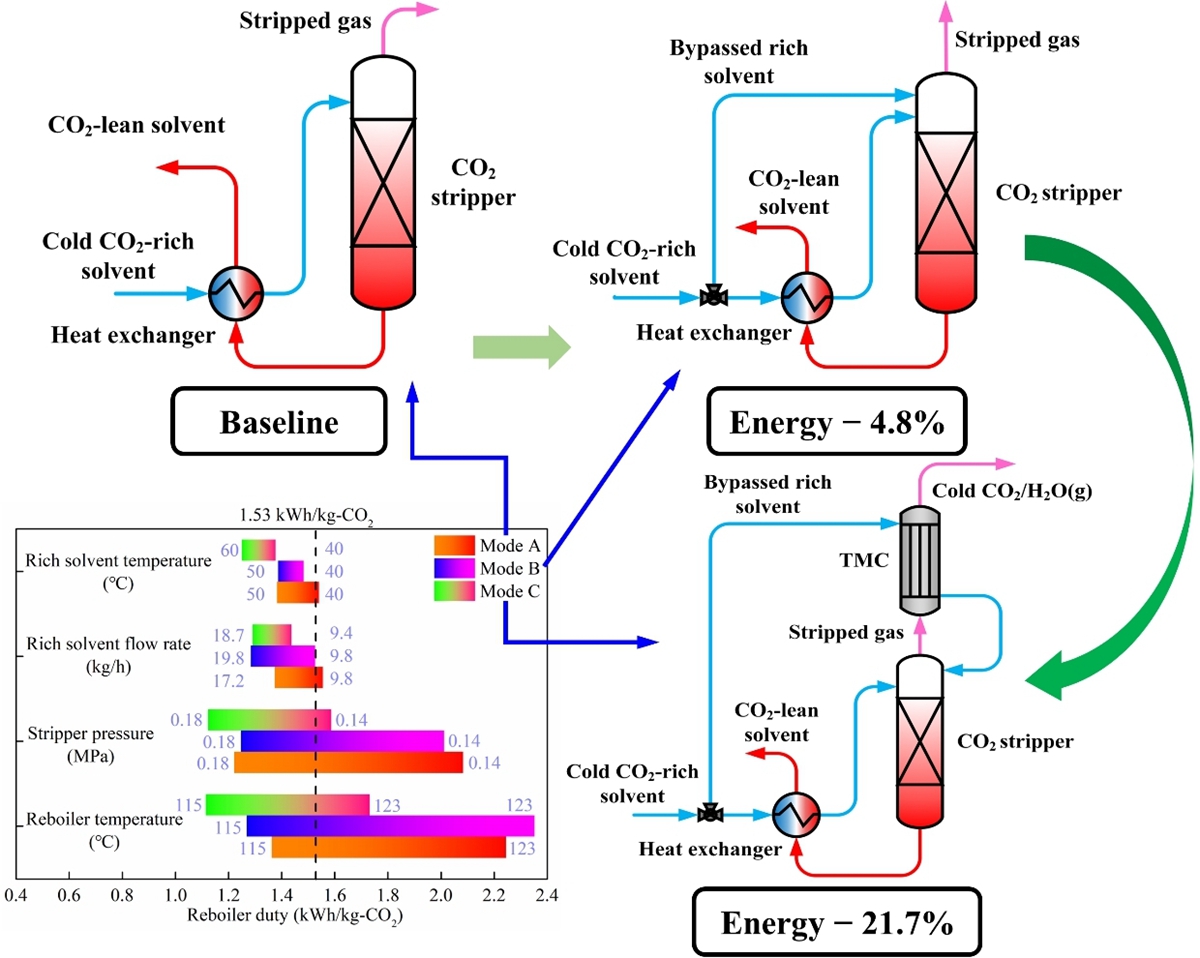
图2 融合跨膜冷凝器的改进型富液分流再生技术的降耗潜力
我校工学院博士生涂特为该论文的第一作者,晏水平教授为该文的通讯作者。该研究得到了国家重点研发计划项目的资助。
论文链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0306261922009011
【英文摘要】
This study proposed to build an energy efficient and reliable CO2 regeneration system, via the integration of an advanced transport membrane condenser (TMC) and principle of rich solvent-split (RS), namely the TMC-based RS system. With the monoethanolamine (MEA) solvent and a TMC module housed commercial 19-channel hydrophilic ceramic membranes, the operational stability and energy requirement of the proposed system were evaluated. With a relatively low error (i.e., ± 5%) of the overall mass balance, the proposed system exhibited excellent reliability in operation. Compared to the traditional CO2 regeneration process without the RS modification, the conventional system with only the RS modification showed 4.8% saving in the reboiler duty (kWh/kg-CO2) at the split fraction of 10%; while the TMC-based RS process showed up to 21.7% saving in the reboiler duty with 0.2 m2 membrane area at the split fraction of 30%. The energy saving corresponded to a decrease from 5.2 MJ/kg-CO2 to 3.9 MJ/kg-CO2 in terms of the calculated CO2 regeneration heat requirement. The sensitivity analysis showed that the TMC-based RS system was less susceptible to variations in operation conditions, demonstrating a low and relatively stable reboiler duty. An additional benefit of the proposed system was the reduced consumption of cooling water.
审核人:晏水平