南湖新闻网讯(通讯员 谭增栋)11月7日,华中农业大学油菜团队联合生物信息团队在Genome Biology发表了题为“Comprehensive transcriptional variability analysis reveals gene networks regulating seed oil content of Brassica napus”的研究论文。该研究全面描述了油菜种子发育过程中转录组变异调控图谱,并结合机器学习与深度学习算法挖掘了油菜种子含油量调控新基因,研究结果为多倍体植物的不对称调控提供了借鉴。
基因表达调控在植物表型和适应性中起着至关重要的作用。遗传变异可以通过影响基因表达进而调控植物的表型,表达数量性状位点(eQTL)研究将基因组变异和基因表达性状联系起来,在解析植物性状的关键基因和调控网络方面发挥了重要作用。群体转录组数据为解析遗传变异到表型架起了桥梁。热点eQTL的解析可以帮助挖掘关键调控因子,最终构建基因调控网络。对于多倍体植物,eQTL也可以帮助解析亚基因组间调控特征。甘蓝型油菜是世界上重要的油料作物,提高种子含油量是油菜重要的育种目标之一。油菜是异源四倍体,基因组十分复杂,含油量基因的克隆和调控网络解析在现阶段依然充满挑战。
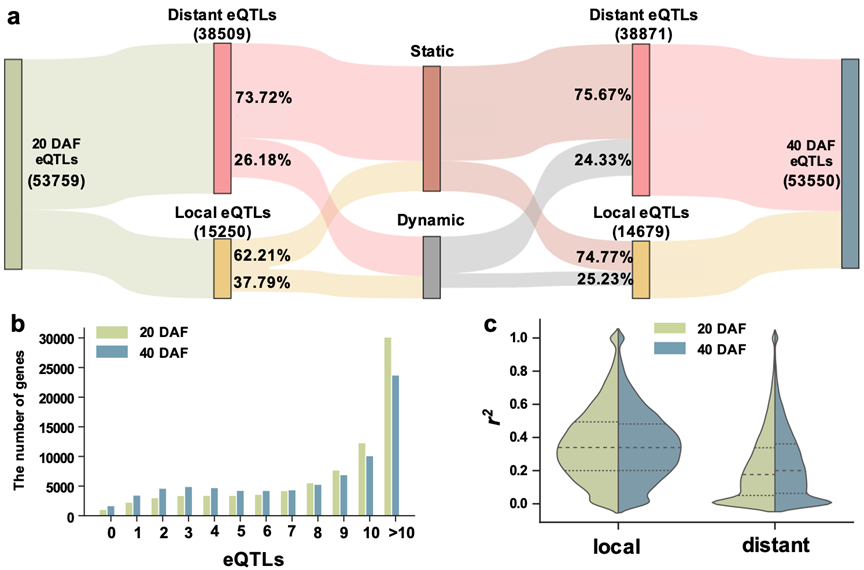
图1 全基因组eQTL动态变化和特征分析
该研究对开花后20天(20 DAF)和40天(40 DAF)两个发育阶段的油菜种子的转录变异进行了全面分析并且构建了调控图谱。在20 DAF和40 DAF分别检测到79,605和76,713个表达的基因以及53,759和53,550个独立的eQTL(图1)。首次在油菜中将eQTL和染色质可及性相结合,发现当相邻的基因对受到local eQTL的调控且具有相同的染色质开放状态时,能表现出更强的基因表达捎带模式。
多倍体植物的亚基因组之间普遍存在不平衡的调节。eQTL分析也为剖析多倍体植物亚基因组间遗传调控和了解异源多倍体亚基因组间同源基因对(HGPs)表达特征提供了丰富的信息。本研究发现油菜An亚基因组相对于Cn亚基因组,具有更丰富的变异和更高的eQTL分布密度。亚基因组间比较分析表明,同源基因对存在反馈调控,以维持部分基因的表达剂量平衡。
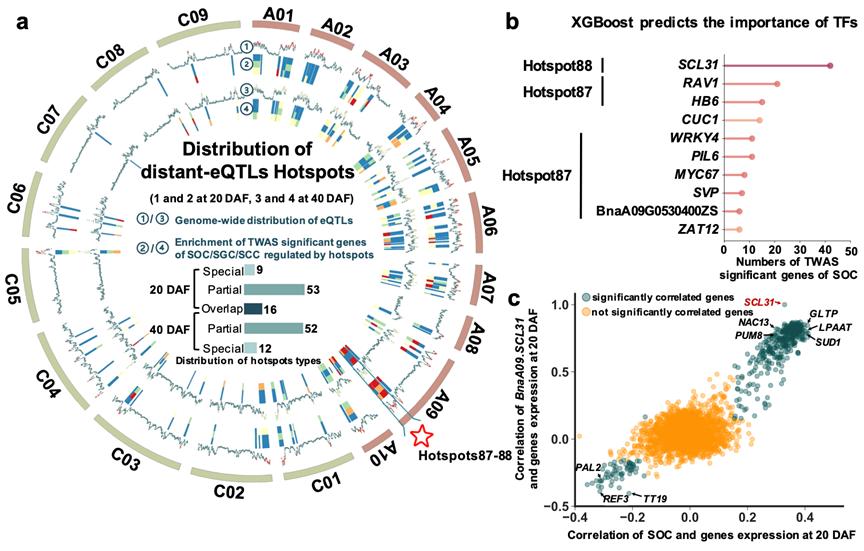
图2 机器学习预测远端热点eQTL调控区中调控含油量的关键转录因子
此外,本研究鉴定了141个热点eQTL,并且在A09染色体上确定了一个影响含油量的关键热点,69.73%的含油量全转录组关联分析显著基因的eQTL与该热点共定位(图2)。为了进一步预测该热点中影响含油量的关键调控因子和调控网络,该研究使用了856个RNA-seq和59个ATAC-seq数据集构建了XGBoost和Basenji模型,预测并验证了转录因子NAC13和SCL31是含油量的正向调控因子。
该研究全面表征了油菜发育中种子的基因调控特征,并构建了油菜eQTL数据库。重点利用多组学分析方法对调控油菜含油量的热点eQTL候选基因进行了预测,成功克隆了两个调控含油量的转录因子,并构建了油菜种子含油量的调控网络。研究结果为多倍体植物的亚基因组不对称调控提供了基础和丰富的遗传资源,也为油菜含油量遗传改良提供重要理论依据。
华中农业大学作物遗传改良全国重点实验室博士生谭增栋为该论文第一作者,赵虎博士、郭亮教授和谢为博教授为该论文通讯作者。德国吉森大学Rod Snowdon教授和Agnieszka Golicz博士、华中农业大学刘克德教授、姚璇副教授和鲁少平副研究员等参与了该研究。该研究受到国家杰出青年科学基金、国家自然科学基金青年基金和湖北洪山实验室重大项目资助。
审核人:郭亮
【英文摘要】
Background
Regulation of gene expression plays an essential role in controlling the phenotypes of plants. Brassica napus (B. napus) is an important source for the vegetable oil in the world, and the seed oil content is an important trait of B. napus.
Results
We perform a comprehensive analysis of the transcriptional variability in the seeds of B. napus at two developmental stages, 20 and 40 days after flowering (DAF). We detect 53,759 and 53,550 independent expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) for 79,605 and 76,713 expressed genes at 20 and 40 DAF, respectively. Among them, the local eQTLs are mapped to the adjacent genes more frequently. The adjacent gene pairs are regulated by local eQTLs with the same open chromatin state and show a stronger mode of expression piggybacking. Inter-subgenomic analysis indicates that there is a feedback regulation for the homoeologous gene pairs to maintain partial expression dosage. We also identify 141 eQTL hotspots and find that hotspot87-88 co-localizes with a QTL for the seed oil content. To further resolve the regulatory network of this eQTL hotspot, we construct the XGBoost model using 856 RNA-seq datasets and the Basenji model using 59 ATAC-seq datasets. Using these two models, we predict the mechanisms affecting the seed oil content regulated by hotspot87-88 and experimentally validate that the transcription factors, NAC13 and SCL31, positively regulate the seed oil content.
Conclusions
We comprehensively characterize the gene regulatory features in the seeds of B. napus and reveal the gene networks regulating the seed oil content of B. napus.
论文链接:https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13059-022-02801-z