南湖新闻网讯(通讯员 周冬冬)近日,我校植物科学技术学院农药毒理团队在Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering期刊上在线发表了题为“Synthesis of bimetallic magnetic complexes for efficient removal of flusilazole”的研究论文。该研究合成了一种新型磁性双金属MOF材料,基于该材料建立了稻田生态系统中常用药剂氟硅唑的快速吸附去除方法。
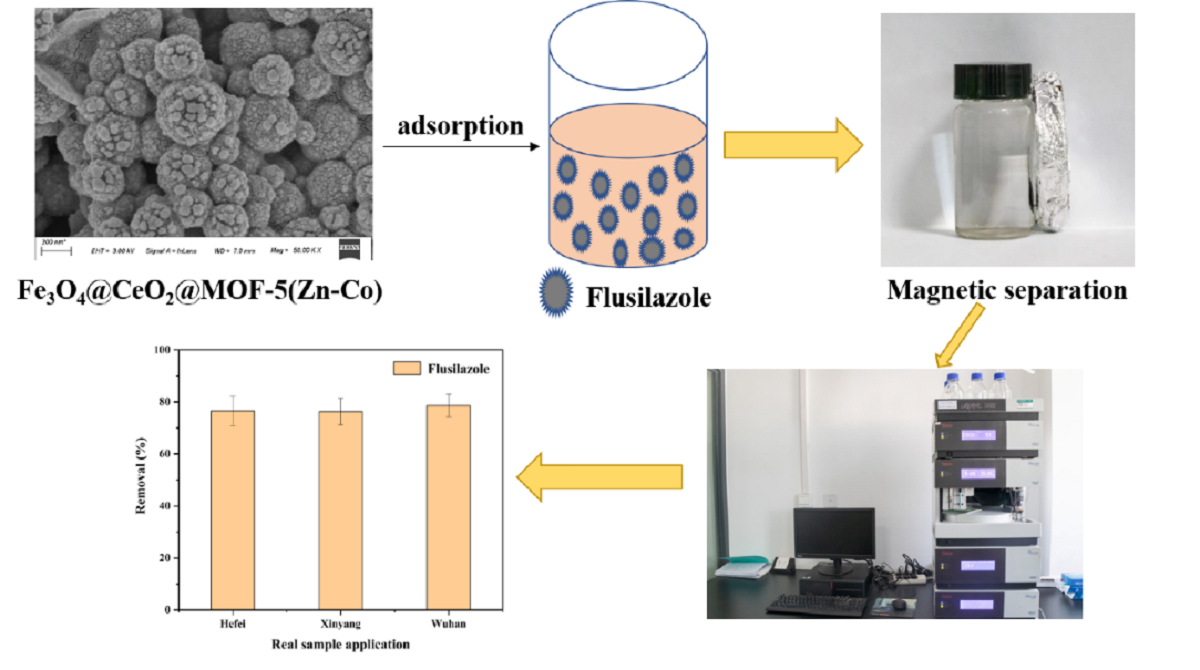
磁性复合材料Fe3O4@CeO2@MOF-5(Zn-Co)的合成及应用
该研究通过CeO2 优异的改性性能以及双金属MOF材料 MOF-5(Zn-Co)的特有优势合成了一种新型的磁性双金属MOF复合材料Fe3O4@CeO2@MOF-5(Zn-Co)。 经FT-IR、TEM、SEM、XRD、VSM和BET等一系列表征分析,证实该双金属磁性MOF材料的吸附性能显著优于传统单一金属MOF材料,且具有更好的化学稳定性及分散性。对氟硅唑的吸附机理研究表明:孔隙填充、表面络合、共价键吸附、π-π相互作用和氢键作用在吸附过程中起作主要作用。此外,经过5次吸附-解吸循环,该吸附剂对目标物质仍能保持较高的去除效率,进一步证实了双金属MOF吸附材料出色的吸附能力和再生能力。作者应用该材料建立了稻田水中氟硅唑残留的有效去除方法,在实际水样加标实验中目标农药去除效率均达85 %以上。本研究合成的Fe3O4@CeO2@MOF-5(Zn-Co)为去除稻田水样中的氟硅唑提供了一种简单可行的方法,并为双金属MOFs材料的应用提出了一种新思路。
近3年该团队在三唑类农药残留研究方面取得了系列成果:在MOF修饰的生物质复合材料研发中,将小麦秸秆变废为宝制成生物炭并与磁性MOF材料结合,制备了可有效去除稻田生态系统中唑类杀菌剂多残留的新型吸附材料,也为绿色环保的吸附剂研发提供了新的思路;在MOF材料与唑类农药吸附机理研究方面,运用DFT计算结合吸附动力学、吸附热力学及XPS等表征分析技术,从分子模拟、理论计算、表征推断、实际验证等多个层面揭示MOF材料特异性吸附唑类农药的机理,为进一步从分子结构出发合成特异性吸附剂打下良好基础;在磁性MOF材料基于的MSPE农药残留快检技术研究中,合成了多种唑类农药特异性吸附剂,将MSPE技术与QuEChERS方法联用,扩大MSPE技术的应用范围,简化QuEChERS方法净化过程,对快速检测食品中农药残留具有重要意义。
植物科学技术学院硕士研究生周冬冬为论文第一作者,杨中华副教授与国家地质实验测试中心田芹教授级高级工程师为共同通讯作者。
论文链接:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2213343722018425?via%3Dihub
【英文摘要】
The purpose of this study was to exploit the advantages of bimetallic MOF material as adsorbents to reduce the potential negative impacts of flusilazole on the environment. Specifically, Fe3O4@CeO2@MOF-5(Zn-Co), which was a magnetic bimetallic MOF composite material, was synthesized and applied as an adsorbent to removal of flusilazole from the environment. The specific surface area and adsorption capacity of this bimetallic magnetic MOF material was proved to be significantly higher than those of traditional single MOF materials. The optimal experimental conditions were obtained by single factor analysis of controlled variables: the amount of adsorbent was 20 mg, the initial pH of the solution was 9.0, and 6% sodium chloride was added. Moreover, the adsorption process was more suitable to be described by pseudo-first-order kinetic model and Langmuir isothermal model. The adsorption mechanisms of Fe3O4@CeO2@MOF-5(Zn-Co) for flusilazole involved pore filling, surface complexation, covalent bonding, π-π stacking effect and hydrogen bonding. After 5 adsorption-desorption cycles, the adsorbent can still maintain a high removal efficiency. Responsibly, the Fe3O4@CeO2@MOF-5(Zn-Co) synthesized in this work provides a simple and feasible method for removal of flusilazole from environmental water samples and proposes an idea for the application of bimetallic MOFs.
审核人:杨中华