南湖新闻网讯(通讯员 曾杨 袁盼) 近日,我校植物营养生物学团队在The Plant Journal发表了题为“Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase 8 increases photosynthesis and seed yield in Brassica napus”的学术论文,揭示了甘蓝型油菜角果光合作用与种子产量形成中海藻糖-6-磷酸合成酶基因BnaC02.TPS8的功能。

海藻糖-6-磷酸(T6P)是植物体中蔗糖有效性和碳代谢的关键信号分子,它在调节蔗糖的利用和分配以及驱动作物生长和产量形成中起着关键作用。T6P合成酶(TPS)可划分为I类和II类,其中I类TPS是植物中合成T6P的关键酶,虽然II类不能直接合成T6P,但它们被认为在海藻糖代谢中起着关键的调节作用。然而,它们在碳代谢和作物产量中的功能仍然未知。
该团队以我国重要油料作物-甘蓝型油菜为研究对象,通过构建转基因材料,探究II类T6P合成酶基因TPS8在碳氮代谢和油菜产量上的功能。结果表明,BnaC02.TPS8主要在甘蓝型油菜成熟叶片和发育中的角果皮中高量表达,亚细胞定位表明其定位于细胞质。与野生型相比,BnaC02.TPS8超表达株系光合作用显著提升,糖、淀粉和生物量的积累显著增加。此外,BnaC02.TPS8促进光合同化物向淀粉和蔗糖的转化,同时减少糖酵解中间产物和有机酸的积累,且该过程与TPS活性呈正相关。田间试验结果表明,无论高氮还是低氮,BnaC02.TPS8均能够提高甘蓝型油菜种子产量,促进种子油脂积累,改善油脂脂肪酸组成。这些结果表明II类TPS对甘蓝型油菜光合作用和种子产量的影响起着重要作用,未来育种中BnaC02.TPS8是提高油菜种子产量的理想靶点之一。
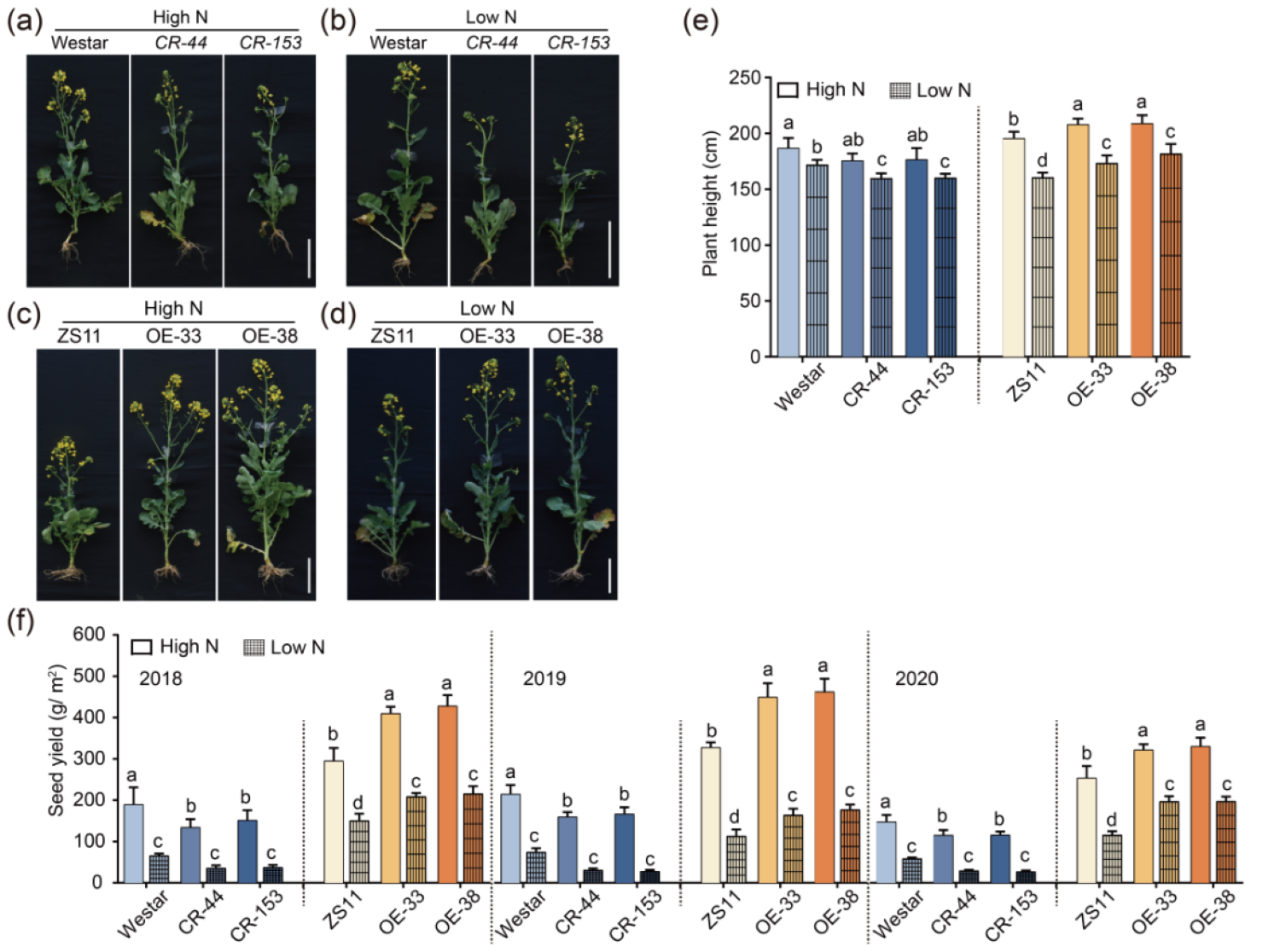
BnaC02.TPS8在甘蓝型油菜种子产量相关性状中起正调控作用
我校博士后袁盼为论文第一作者,石磊教授为论文通讯作者。我校已毕业硕士生余明珠,博士生周贵龙、刘海疆,团队蔡红梅副教授、汪社亮副教授、王创教授、徐芳森教授,洪登峰教授、英国雷丁大学John P. Hammond教授也参与了该项研究。该研究得到了国家自然科学基金和国家留学基金委项目的资助。
审核人:石磊
【英文摘要】
Trehalose-6-phosphate (T6P) functions as a vital proxy for assessing carbohydrate status in plants. While class II T6P synthases (TPS) do not exhibit TPS activity, they are believed to play pivotal regulatory roles in trehalose metabolism. However, their precise functions in carbon metabolism and crop yield have remained largely unknown. Here, BnaC02.TPS8, a class II TPS gene, is shown to be specifically expressed in mature leaves and the developing pod walls of Brassica napus. Over expression of BnaC02.TPS8 increased photosynthesis and the accumulation of sugars, starch, and biomass compared to wild type. Metabolomic analysis of BnaC02.TPS8 overexpressing lines and CRISPR/Cas9 mutants indicated that BnaC02.TPS8 enhanced the partitioning of photoassimilate into starch and sucrose, as opposed to glycolytic intermediates and organic acids, which might be associated with TPS activity. Furthermore, the overexpression of BnaC02.TPS8 not only increased seed yield but also enhanced seed oil accumulation and improved the oil fatty acid composition in B. napus under both high nitrogen (N) and low N conditions in the field. These results highlight the role of class II TPS in impacting photosynthesis and seed yield of B. napus, and BnaC02.TPS8 emerges as a promising target for improving B. napus seed yield.
原文链接