南湖新闻网讯(通讯员 董晓茹)近日,我校水产学院鱼类遗传育种与繁育实验室高泽霞教授课题组以模式生物斑马鱼为研究对象,揭示了鱼类骨形态发生蛋白 7 (BMP7) 中bmp7a和bmp7b亚型功能上的分化。相关研究成果以“Functional differentiation of bmp7 genes in zebrafish: bmp7a for dorsal-ventral pattern and bmp7b for melanin synthesis and eye development”为题在Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology发表
曾有科学研究揭示,骨形态发生蛋白 7 (BMP7) 属于转化生长因子 β (TGF-β) 家族,不仅能诱导软骨和骨形成,还能调节哺乳动物的眼睛发育和黑色素瘤的发生(Luo et al 1995;Rothhammer et al 2005;Lavery et al 2009)。硬骨鱼中BMP7分化为了bmp7a和bmp7b亚型,我校科研人员认为硬骨鱼中bmp7a和bmp7b各自发挥什么样的作用很值得探究。
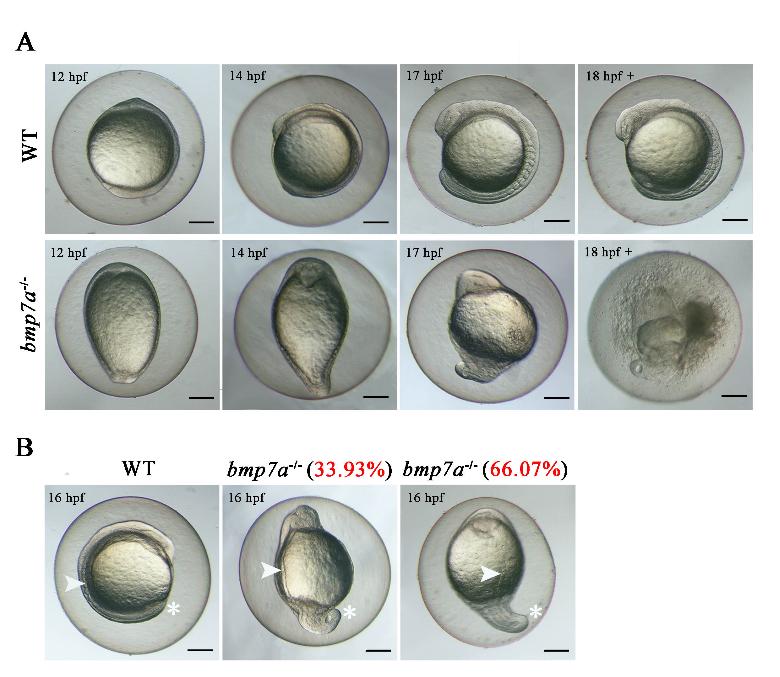
野生型和bmp7a-/-突变体胚胎中的纯合致死表型观察
在研究中,我校科研团队通过CRISPR/Cas9介导的基因敲除技术在斑马鱼中构建了bmp7a和bmp7b纯合突变品系。发现其中bmp7a-/-突变体胚胎的背腹模式发育异常,从而在胚胎期发生死亡。Bmp7b-/- 突变体生长受到抑制,皮肤和眼睛视网膜中黑色素增多,摄食行为受到阻碍。
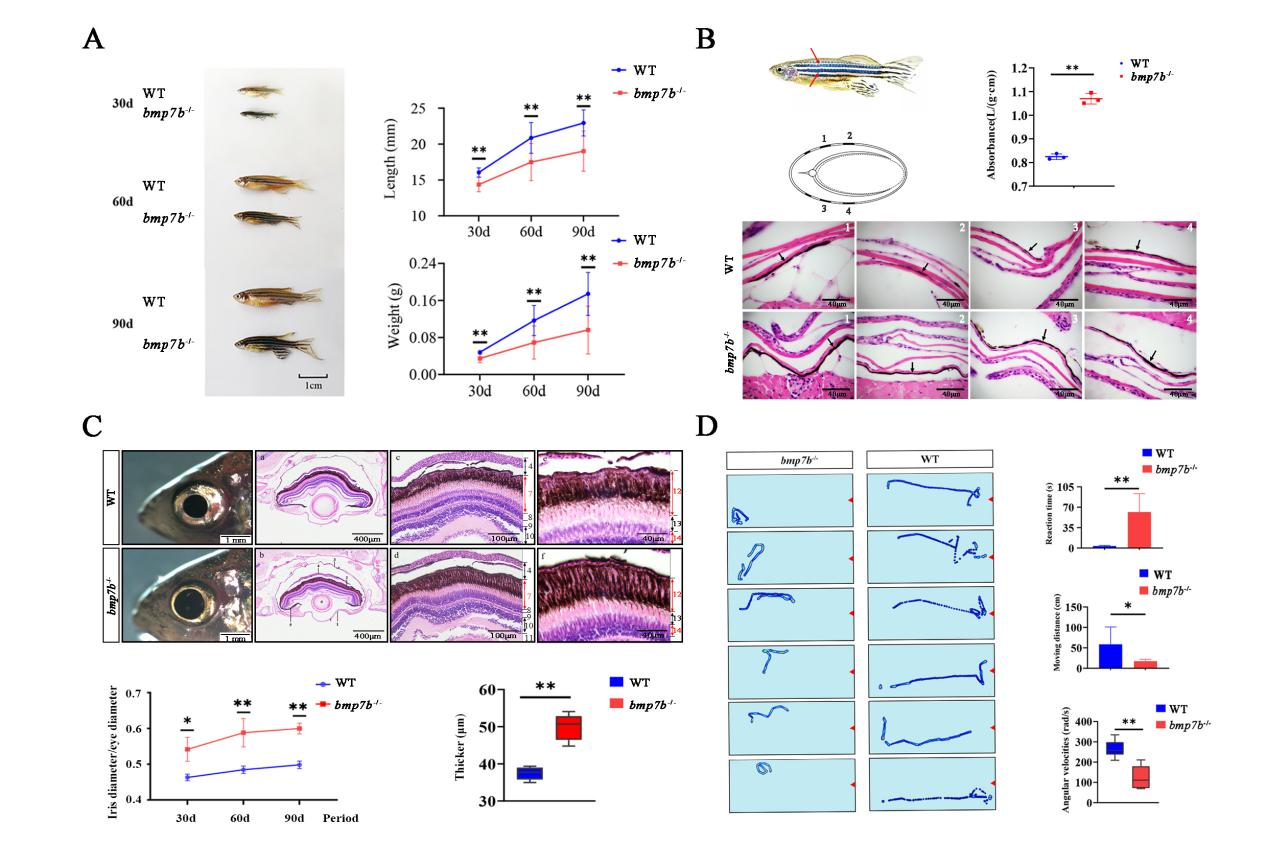
野生型和bmp7b-/-突变体的表型观察
研究人员进一步探究了Bmp7b-/- 突变体的皮肤和眼组织的转录组的相关调控机制,认为wnt7ba和gna14等基因的表达变化可能促进黑色素的增加,而眼睛结构的变化导致光转导缺陷,并且 7 个 DEGs(rgs9a、rgs9b、rcvrn2、guca1d、grk1b、opn1mw4 和 gc2)被确定为关键候选基因,影响眼睛的光响应。
通过这项研究,科研人员揭示了bmp7a和bmp7b在硬骨鱼中的功能分化,首次报道bmp7b对黑色素生成的抑制作用,并认为这项发现可能为未来人类黑色素瘤相关疾病的研究提供有用的信息。
该研究获得了湖北洪山实验室、国家现代农业产业技术体系、国家自然科学基金等项目的支持。
审核人:高泽霞
【英文摘要】
Bone morphogenetic protein 7 (BMP7) belongs to the transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) family, which not only induces cartilage and bone formation, but also regulates eye development and melanoma tumorigenesis in mammals. In teleosts, BMP7 differentiates into two subtypes, bmp7a and bmp7b, which have clearly differentiated structures. To fully understand the functional differentiation of bmp7a and bmp7b in fish species, we successfully constructed bmp7a and bmp7b gene deletion mutants in zebrafish using CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing technology. Our results showed that bmp7a mutation caused abnormal development of the embryo’s dorsal-ventral pattern that led to death; bmp7b mutation induced growth inhibition and increased melanin production in the skin and eye of mutants. Histological analysis revealed that melanin in the retina of the eyes in bmp7b mutants increased, and behavioral observation showed that the vision and sensitivity to food of the mutants were reduced. Transcriptome analysis of the skin and eye tissues showed that the expression changes of wnt7ba and gna14 in bmp7b mutants might promote the increase of melanin. Additionally, the eye transcriptome analysis indicated that changes in the structure of the eyes in bmp7b mutants led to defects in phototransduction, and seven DEGs (rgs9a, rgs9b, rcvrn2, guca1d, grk1b, opn1mw4, and gc2) were identified as key candidate genes that affected the photonic response of the eyes. The study revealed the functional differentiation of bmp7a and bmp7b in teleosts and the first report about the inhibitory effect of bmp7b on melanogenesis may provide useful information for the future research on human melanoma-related diseases.
