南湖新闻网讯 (通讯员 路莹莹)近日,我校理学院廖水姣副教授带领的环境材料团队通过施用甜叶菊渣协调蜈蚣草实现砷污染土壤的高效植物修复。相关研究成果发表在Journal of Hazardous Materials上。
土壤重金属污染的植物修复因环境友好等优点近年来受到环境领域的广泛关注,但因存在修复效率低的瓶颈而推广受限。甜叶菊渣(SR)属甜叶菊提取甜菊糖苷后的废弃物,其富含N、P、K、Ca等营养物质可促进蜈蚣草的生长,其含丰富的可溶性有机物DOC能将土壤中不可利用的砷转化成土壤可利用态砷;能影响土壤微生物群落的多样性,如使砷污染土壤中假单胞菌属(Pseudomonas)和厌氧菌(Anaerobes)所占比例显著提高,因而增加土壤生物可溶性砷含量,鞘脂单胞菌属(Sphingomonas)所占比例显著提高,其分泌的植物激素(GAS, IAA)可促进蜈蚣草的生长。研究结果表明,添加甜叶菊渣的处理蜈蚣草修复砷污染土壤的效率提高了91.06%,一年内可达10.26%。本研究提出了甜叶菊渣介导的提高蜈蚣草提取砷能力的潜在机制,为土壤砷污染修复提供了一种新的经济环保的方法。
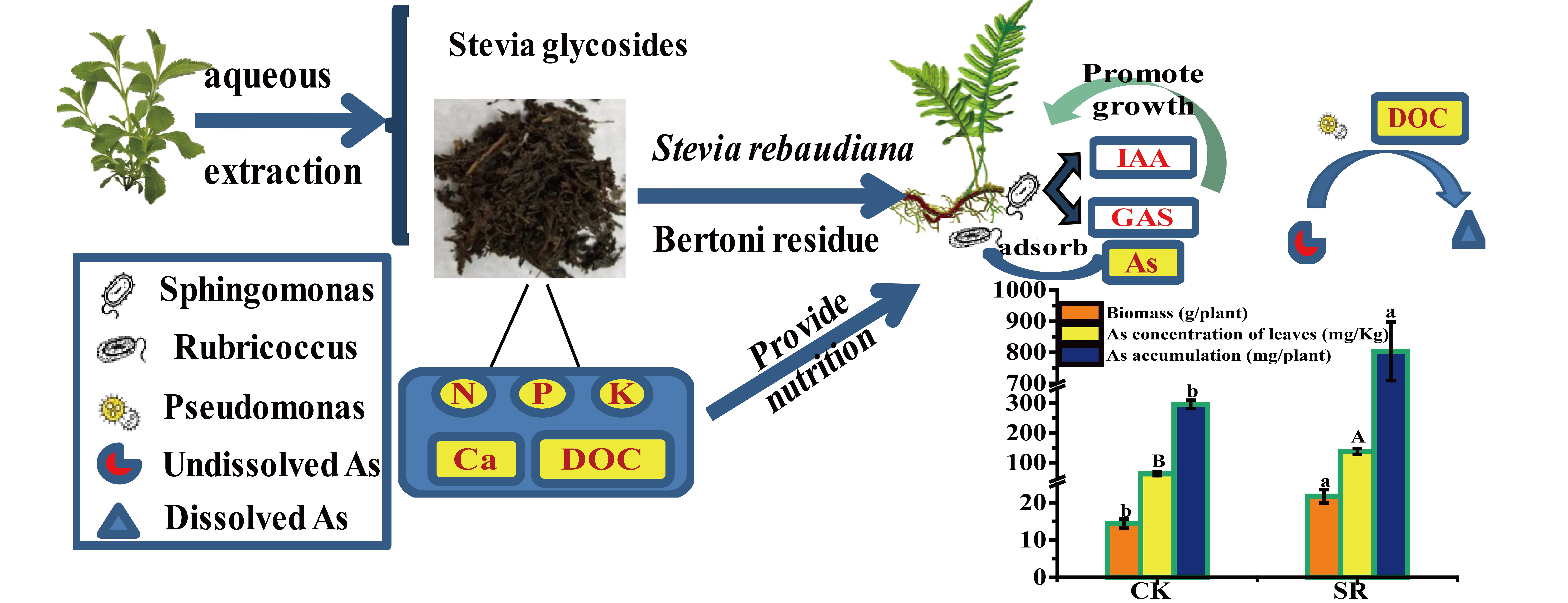
图1甜叶菊渣提升蜈蚣草修复砷污染土壤效率及可能的机制
路莹莹博士为论文第一作者,廖水姣副教授为通讯作者。本研究得到了国家重点研发专项基金项目(2017YFD0801303,2016YFD0800802)资助。
此外, 本研究团队针对土壤重金属污染治理难度大的问题,发明了用 WH16-1菌固定土壤重金属的方法并验证了其作用机理,相关专利成果已获授权(ZL201510297134.9),论文发表在Water Air Soil Pollut (DOI : 10.1007/s11270-016-3040-7)。微生物修复土壤重金属污染技术中微生物菌剂容易失活贮存稳定性差的问题,发明了用莲房和海藻酸钠制备固定化WH16-1菌的方法,发现了固定化菌具有优于游离菌的重复利用性和贮存稳定性,对土壤中鎘有显著的固定效果使稻米中镉含量显著地降低了78.31 %,提出了固定化菌去除镉的模型。研究提供了一种经济环保的微生物固定化技术。相关专利成果已获授权(ZL201710787339.4),论文发表在 Journal of Hazardous Materials(2018, 357: 431)。
英文摘要:
Soil contamination by arsenic (As) presents a high risk to public health, necessitating urgent remediation. This study sought to develop an efficient strategy for the phytoremediation of As-contaminated soil. The effects of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni residue (SR) on the available As (A-As) concentration of soil and As extraction from the soil by Pteris vittata L. were studied by soil simulation, pot, and field experiments. The A-As concentration in the soil simulation experiment increased significantly by 84.20 % after 20 days. The biomass, As concentration, and total extracted As of SR-treated P. vittata L. in the pot experiment increased significantly by 50.66 %, 120.2 %, and 171.2 %, respectively, compared to the untreated control. The SR-treated rhizosphere soil in the pot experiment displayed a significant 21.72 % decrease in total As concentration. In the one-year field experiment, treatment with SR resulted in a significant 191.1 % increase in As extraction by P. vittata L. and a significant 10.26 % reduction in rhizosphere soil As concentration compared to the control. This study proposes a potential mechanism for SR-mediated enhancement of P. vittata L. As extraction ability and provides a new, economic, and environmentally friendly method for As-contaminated soil remediation.
论文链接:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126678
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.06.027
审核人:廖水姣
